- In-Stock Tumor Cell Lines
- Human Orbital Fibroblasts
- Human Microglia
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Valvular Interstitial Cells
- Human Thyroid Epithelial Cells
- C57BL/6 Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Alveolar Macrophages
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Lung Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Retinal Muller Cells
- Human Articular Chondrocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
- Human Kidney Podocyte Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
Diabetes and Cell Therapy
Diabetes is a global disease characterized by high sugar, which has two subtypes: Type 1 (Type I) Diabetes and Type 2 (Type II) Diabetes. Diabetics are very vulnerable to other cancers and infections in which a high sugar environment will promote the long-term proliferation of bacteria.
Cell Therapy is a field of medicine that involves injecting intact, living cellular material directly into a patient for the treatment of disease.
Islets of Langerhans are the endocrine part of the pancreas, which are irregular cell groups scattered in the pancreas. Some studies have shown that islet cells may play a vital role in the treatment of diabetes. Therefore, separating the islets of Langerhans cells correctly and effectively is very critical in the treatment of diseases.
How to Isolate Islets of Langerhans Cells?
Isolation of pancreatic islet cells was performed by using standard collagenase digestion and gradient purification[1, 2]. After the isolation, the isolated islets were stain with chromogranin A (CgA) antibodies, which were islet cell markers and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the percentage of islet cells or used trypan blue staining for cell activity[3]. Finally, different subtypes of islet cells were sorted by flow cytometry or magnetic bead sorting. So you know the proportion of alpha cells (α-cells), beta cells (β-cells), and delta cells and so on in islet primary cells, and these cell characteristics analyzed by single-cell sequencing[4].
As shown in figure1, the delta-cells, β-cells, and alpha-cells respectively account for 1–5%, 70%, and 5-10% of the total islet cells that the rest are uncertain cell types in human islets. The percentage of beta cells fall within the expected range of islet cell distributions for the mouse endocrine pancreas[5].
Islet beta cells are stored in particular cytoplasmic secretory vesicles with an electronic core and a clear peripheral envelope, and delta-cells are located in the mantle closer to the outer islands while in individuals they are distributed throughout the islets[6]. They are closely related to diabetes and will further explain the function of these cells, which reveals the relationship with diabetes.
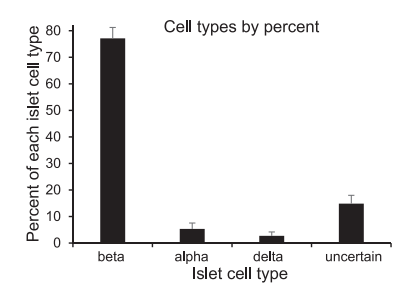
Figure1. The proportion of four different endocrine cells after isolation and purification of islet cells. [5].
Type I Diabetes, β-Cells, and Islet Transplantation
Beta-cells (β-cells) can regulate intracellular Ca2+ and thereby regulate insulin concentration in response to glucose levels[7]. Disruption or dysfunction of beta cells can cause diabetes[8], Patients with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) lose 70–90% of their pancreatic β-cells.
The best causative treatment for T1D would be to increase the number of functional β-cells, so the success rate of transplanting islet cells for diabetic patients may be exceedingly increased if a large number of mature beta cells could be cultured in vitro.
Aydin’s results revealed that boron-containing compounds might be used to protect pancreatic β-cells from damages caused by hypoxic conditions. In the future, boron-containing drugs could be developed to decrease insulin dependency on type 1 diabetes patients[9].
Nair’s research may increase the efficiency of islet transplantation so that diabetic patients can use the technology of islet cell transplantation to allow the body to self-regulate blood sugar and abandon the hypoglycemic agent[9].
Nair et al. found a method for culturing mature human beta cells in vitro while they isolated eBCs cells exhibited normal human beta cell characteristics in vitro: the beta cells will develop into a “juvenile” functional state after birth, and the insulin secretion capacity of the “juvenile” human beta cells will continue to increase until adolescents such as MAFA, SIX2, and SIX310, 15 are enriched. The high expression of MAFB in young beta cells indicates that the gene plays an indispensable role in obtaining initial function[10].
Meanwhile modified α-cells revealed expression signatures intermediate between α-cells and β-cells and the transplantation of reprogrammed human α-cells into diabetic mice ameliorated clinical signs of diabetes[11].
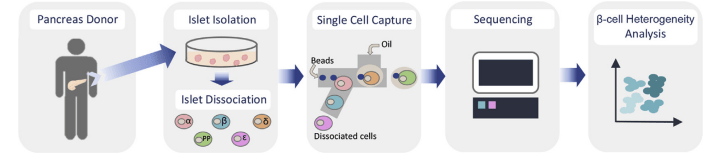
Figure2. Graphical workflow for large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing of human islet cells. Pancreatic islets were obtained from cadaver organ donors; Islets were cultured and subsequently dissociated into single cells; sequencing was performed to the appropriate specifications; Single-cell sequencing data were processed; Further analysis to identify cell clusters, cell-type subpopulations, and cluster enriched genes among others[4].
Delta Cells (δ-cells)
Delta cells are critical paracrine regulators of beta-cell and alpha-cell secretory activity, and δ-cells can modulate beta-cell activity under physiological conditions. It has been reported that δ-cells transform into β-cells in the condition of a sharp decrease of β-cells mass.
Delta cells indirectly affect the control of glucose homeostasis in health and disease[12]. Studies have shown that diabetes is associated with impaired somatic growth hormone release or death of delta cells.
Drigo et al. found that healthy and pre-diabetic delta cells can effectively exert an active inhibitory force on islet β and α cells that serve as practical regulators of glucose homeostasis in diabetes [13].
Although δ cells also regulate α cells and could be transdifferentiated into β cells that made decreased the quality of δ cell, the current evidence does not support the transdifferentiation of δ cells into β cells [11]. Therefore, researchers are almost always research beta cells during the treatment of diabetes.
Conclusion
Recently, pluripotent stem cells have the potential to produce an unlimited number of beta cells and could be used for diabetes treatment. Therefore, a large number of beta-cells and delta-cells will be used for islet transplantation, and these cells collectively regulated the concentration of blood sugar that the treatment of diabetes may also change.
AcceGen Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
AcceGen provides Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells, which were derived from human pancreas.
To support your research, AcceGen cryopreserves our human primary cells in second passage for the best viability and plating efficiency. In addition, all donors from which the cells were derived were pre-screened.
For more detailed information, please visit our website or contact [email protected]
References
- Saliba Y, Fares N: Isolation, Purification, and Culture of Mouse Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans. Methods Mol Biol 2019, 1940:255-265.
- Loganathan G, Subhashree V, Narayanan S, Tweed B, Andrew Goedde M, Gunaratnam B, Tucker WW, Goli P, Mokshagundam S, McCarthy RCet al: Improved recovery of human islets from young donor pancreases utilizing increased protease dose to collagenase for digesting peri-islet extracellular matrix. Am J Transplant 2019, 19(3):831-843.
- Sayadi LR, Alexander M, Sorensen AM, Sarantopoulos N, Lau H, Klopfer M, Ziegler ME, Banyard DA, Evans GRD, Lakey JRTet al: Micro/nanobubbles: Improving Pancreatic Islet Cell Survival for Transplantation. Ann Plast Surg 2019, 83(5):583-588.
- Dominguez-Gutierrez G, Xin Y, Gromada J: Heterogeneity of human pancreatic beta-cells. Mol Metab 2019, 27S: S7-S14.
- Scarl RT, Corbin KL, Vann NW, Smith HM, Satin LS, Sherman A, Nunemaker CS: Intact pancreatic islets and dispersed beta-cells both generate intracellular calcium oscillations but differ in their responsiveness to glucose. Cell Calcium 2019, 83:102081.
- Tran Thi Nhu H, Arrojo EDR, Berggren PO, Boudier T: A novel toolbox to investigate tissue spatial organization applied to the study of the islets of Langerhans. Sci Rep 2017, 7:44261.
- Katarzyna Cierpka-Kmiec1 AW, Zbigniew Kmiec2: In vitro generation of pancreatic b-cells for diabetes treatment. I. b-like cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells. FOLIA HISTOCHEMICAET CYTOBIOLOGICA 2019, 57.
- LICKERT FJTH: A map of β-cell differentiation.Nature 2019, 569.
- Aydin S, Demirci S, Dogan A, Sagrac D, Kasikci E, Sahin F: Boron containing compounds promote the survival and the maintenance of pancreatic beta-cells. Mol Biol Rep 2019, 46(5):5465-5478.
- Luciano AK, Guertin DA: Oncogenic AKTivation by methylation. Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21(2):114-115.
- Furuyama K, Chera S, van Gurp L, Oropeza D, Ghila L, Damond N, Vethe H, Paulo JA, Joosten AM, Berney Tet al: Diabetes relief in mice by glucose-sensing insulin-secreting human alpha-cells. Nature 2019, 567(7746):43-48.
- Rorsman P, Huising MO: The somatostatin-secreting pancreatic delta-cell in health and disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018, 14(7):404-414.
- Arrojo EDR, Jacob S, Garcia-Prieto CF, Zheng X, Fukuda M, Nhu HTT, Stelmashenko O, Pecanha FLM, Rodriguez-Diaz R, Bushong Eet al: Structural basis for delta cell paracrine regulation in pancreatic islets. Nat Commun 2019, 10(1):3700.

Copyright - Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are AcceGen™ All Rights Reserved – Full details of the use of materials on this site please refer to AcceGen Editorial Policy – Guest Posts are welcome, by submitting a guest post to AcceGen you are agree to the AcceGen Guest Post Agreement – Any concerns please contact [email protected]