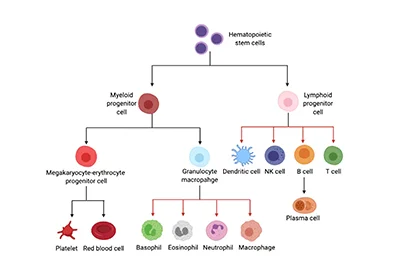
- In-Stock Tumor Cell Lines
- Human Orbital Fibroblasts
- Human Microglia
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Valvular Interstitial Cells
- Human Thyroid Epithelial Cells
- C57BL/6 Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Alveolar Macrophages
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Lung Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Retinal Muller Cells
- Human Articular Chondrocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
- Human Kidney Podocyte Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
Abstract
Tumor cells can seriously affect the prognosis of tumor patients for having the features of unlimited proliferation, resistance to apoptosis, and dedifferentiation. Therefore, we conducted researches on the influence of the expression level of some tumor-related factors on the proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Further, provide some reference data for gene therapy for esophageal cancer patients.
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is an extremely high-risk disease that is very easy to invasive. According to research, about 50% of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma were Chinese, but researches on targeting and immunotherapy in China was very rare. Although surgical radiotherapy and chemotherapy have made great progress in the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, the survival rate of patients has not significantly improved. The cell lines currently used for research such as KYSE30 cell, KYSE150 cell , KYSE240 cell, and KYSE150 cell were established by Shimada et al. which were isolated from tumor tissues of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gradually cultured into the esophageal cancer cell line we currently apply.


Fig 1. Morphological of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells
-
1.Inflammatory signaling pathway affects proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells
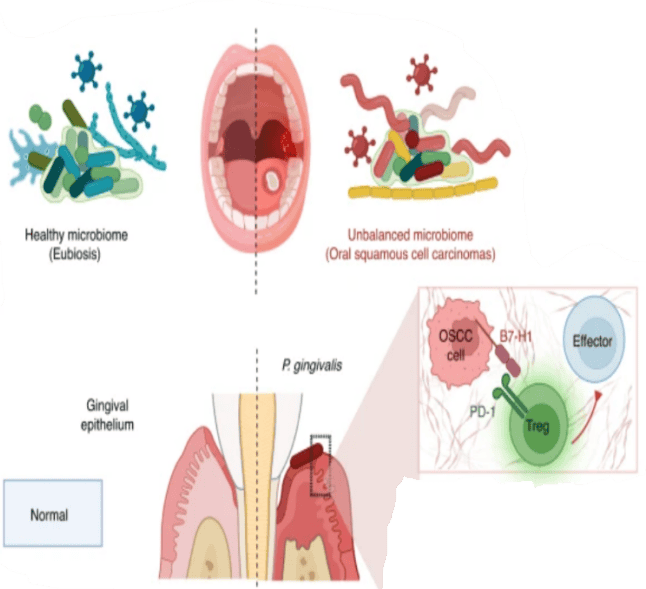
Studies have shown that smoking, diet, and other risk factors can alter the occurrence and expansion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. These inflammatory factors can activate the transcription of genes downstream of the signal through signal transduction, further promoting the proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Recent studies have revealed new target factors for the IL-6 pathway. Chen et al. found that silencing B7-H4 can significantly reduce IL-6 secretion by regulating B7-H4 expression levels in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines such as Eca109cells, TE1 cells, and TE13 cells proliferation. Thus, B7-H4 promotes the proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells through the IL-6 signaling pathway. It may be one of the molecular mechanisms of B7-H4 in ESCC development and poor prognosis. At the same time, Li et al. found that PMS drugs can inhibit the expression of IL-6, human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca-109, TE-1 cell lines proliferation, and can also inhibit IL-6-mediated EMT metastasis. PMS passed NF- κB signaling pathway inhibits the expression of IL-6 and was intended to reveal that PMS may be an effective drug for human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. These investigations have shown that further studies can be carried out on the IL-6 signaling pathway in the later stage. We may find effective targets from these signaling pathways and play a significant role in the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Fig2. B7-H3 and B7-H4 promoted T cells to secrete immunosuppressive cytokines to maintain a tumor microenvironment.
-
2.Non-coding RNA regulates the proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines
Experimental investigations have shown that non-coding RNA and transcription factors were involved in the development of many diseases. Non-coding RNA can influence the transcription and translation of downstream genes. Non-coding RNA’s modifications in cells can be used as markers for some malignant lesions. These characteristics may be a target for the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Song found that high expression of circRNA has-circ-0000337 can promote the proliferation and invasion of human esophageal cancer KYSE-150 and TE-1 cell lines. Reverse knockdown of circ RNA has-circ-0000337 inhibits the proliferation of ESCC cell lines but promotes apoptosis. Suggesting that miR-1269a can be used as a possible target for the diagnosis of esophageal squamous cells, miR-1269a can be promoting the proliferation of KYSE 30 cell line by inhibiting the expression of SOX6. These studies imply that certain non-coding RNAs can serve as potential diagnostic targets for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and potential therapeutic targets for biotherapeutic therapy.

Fig3. Expression of hsa_circ_0000337 in ESCC tissues and cell lines.
Notes: (A) The Wilcoxon signed-rank test showed that the expression of hsa_circ_0000337 in cancer tissues was upregulated compared to matched adjacent normal-appearing tissues. (B) The expression of hsa_circ_0000337 in the esophageal carcinoma cell line TE-1 was higher than that in the normal human esophageal epithelial cell line HET-1A, but was not significantly changed in KYSE-150. (C) There was a slight upward trend when comparing clinical samples with poor to well differentiation grades. The three lines in (A) and (C) represent the median with interquartile ranges. 1: moderate-poor or poor differentiation; 2: moderate differentiation; ands3: well-to-moderate or well-differentiation. **P<0.01.
-
3.Transcription factor expression level regulates proliferation and differentiation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cell lines
Reihaneh found that after knocking down the Meis1 gene, it promoted the differentiation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma KYSE-30 cell lines, indicating that inhibition of Meis1 gene expression can be a useful therapeutic strategy for ESC cell proliferation and invasion. Meanwhile, Nishimura found that the transcription factor SIX1 was abnormally highly expressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, which can cause high expression of TGF-β and its receptor. Subsequent studies have found that knockdown of the SIX1 gene can attenuate tumor invasion and slow down its growth rate. High HFI-1 expression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma caused by HFI-1 can adapt their tumor cells to a hypoxic environment which resulted from poor prognosis. Zhu found that the extension of HFI-1 inhibitor PX-478 can significantly inhibit esophageal squamous cell carcinoma EC109 cell lines proliferation, EC9706 cell lines proliferation, and promote their apoptosis. All of these findings and references are valuable to clinical treatment.
 Fig4. Representative pictures of IHC staining of HIF-1α (A, 0; B, 1+; C, 2+; D, 3+), COX-2 (E, Positive; F, Negative) and PD-L1 (G, Positive; H, Negative) in tissue sections of ESCC. COX-2 expression was primarily localized to the cytoplasm of cancer cells, while HIF-1α expression was observed in both cytoplasm and nucleus of cancer cells and PD-L1 expression in the cytoplasm and membrane of cancer cells.
Fig4. Representative pictures of IHC staining of HIF-1α (A, 0; B, 1+; C, 2+; D, 3+), COX-2 (E, Positive; F, Negative) and PD-L1 (G, Positive; H, Negative) in tissue sections of ESCC. COX-2 expression was primarily localized to the cytoplasm of cancer cells, while HIF-1α expression was observed in both cytoplasm and nucleus of cancer cells and PD-L1 expression in the cytoplasm and membrane of cancer cells.
Conclusion
The expression level of tumor-associated factors significantly affects the proliferation and apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Studies upon tumor-related factors will help us to expand our understanding of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and provide references for the exploration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. In the future, with the development of targeted drugs, biological immunotherapy, and angiogenesis normalization in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, the effects of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its related molecular expression on esophageal cancer will be further understood, and there will be more options regarding the treatment of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
AcceGen Products
AcceGen provides high quality esophageal cancer cell lines to support related research. More information please find on our website or contact [email protected].

Copyright - Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are AcceGen™ All Rights Reserved – Full details of the use of materials on this site please refer to AcceGen Editorial Policy – Guest Posts are welcome, by submitting a guest post to AcceGen you are agree to the AcceGen Guest Post Agreement – Any concerns please contact [email protected]