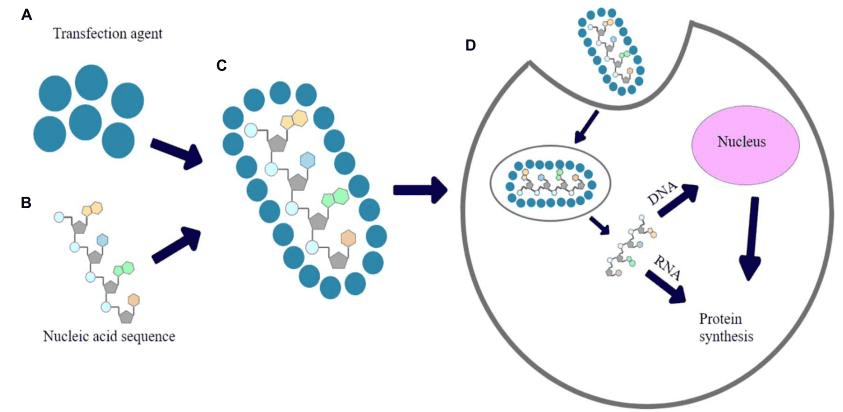
- In-Stock Tumor Cell Lines
- Human Orbital Fibroblasts
- Human Microglia
- Human Pulmonary Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Colonic Fibroblasts
- Human Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cells
- Human Valvular Interstitial Cells
- Human Thyroid Epithelial Cells
- C57BL/6 Mouse Dermal Fibroblasts
- Human Alveolar Macrophages
- Human Dermal Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Lung Fibroblasts, Adult
- Human Retinal Muller Cells
- Human Articular Chondrocytes
- Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans Cells
- Human Kidney Podocyte Cells
- Human Renal Proximal Tubule Cells
The Relationship between Breast Cancer and Breast Cancer Cells
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death among women in developed countries[1]. The majority of breast cancer patients are over 50 years old. However, the result of new cases study shows that the number of breast cancer patients under 45 years old has exceeded 10%[2].
Currently, most of the breast cancer knowledge comes from in vivo and in vitro studies using breast cancer cell lines because they can provide unlimited amounts of homologous self-replicating material using simple but standard media[3]. Therefore, it is essential to know whether these cell lines can capture molecules well before obtaining any clinically relevant results.
Breast Cancer MDA-MB-series Cell Lines Establishment
MDA-MB- series tumor cell lines were established from M. D. Anderson Hospital and Tumor Institute. They have created a total of 19 MDA-MB series of cell lines from female patients with breast cancer, of which sixteen (16) MDA-MB cell lines were established from a pleural effusion (MDA-MB-134/468/469/157/231/436/435S/330/415/175-VII/253/309/431/416/411/390), two (2) cell lines from brain metastases (MDA-MB-361, MDA-MB-461), and one (1) breast cancer cell line from heart cells liquid (MDA-MB-453). The 19 MDA-MB- series tumor cell lines can be divided into several types according to different growth rates and growth conditions[4].
Among all the mentioned MDA-MB- series breast cancer cell lines, MDA-MB-231 cell line has a more fragmented mitochondrial reticulum but does not express ERα, PR, and neither HER’s-2. MDA-MB-231 cell line can be used as a representative of triple-negative breast cancer, which is the most aggressive breast cancer subtype and display high metastatic potential. Therefore, many researchers use the MDA-MB-231 cell line to study breast cancer proliferation and invasion.
The Origin of Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231
Human breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 is an epithelial cell that adheres to the growth, and it is a triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell. MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell was isolated from the pleural fluid of a 51-year-old white female breast cancer patient [5].

Figure1. The molecular characteristics of the cell lines[6]. The MDA-MB-231 is triple-negative (ER, PR, and HER2 negative).
A Better Method to Cultivate MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line
Human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 was maintained in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FCS, 2mM L-glutamine, and 100U/ml penicillin-streptomycin. Cells were cultured in the humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 and passaged when they reached 80–90% confluence[7].
As shown in figure2, breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 grow randomly in a spindle-shaped[8]. MDA-MB-231 cells can survive for two days without glucose, but cannot survive in the absence of glutamine[9]. Therefore, researchers should remember to add 2mM glutamine L-glutamine to the medium when investigating MDA-MB-231 cells.

Figure2. The cell morphology of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 cells[8].
The Features and Applications of MDA-MB-231 Cells
MDA-MB-231 is one of the most studied estrogen receptor (ER) negative breast cancer cell lines [10]. TNBC cell MDA-MB-231 has a more fragmented mitochondrial reticulum, leading to increased migration and invasion capacities[11]. Therefore, researchers often use MDA-MB-231 cells to research the mechanism of breast cancer [12].
For example, anticancer agents such as All-trans retinoic acid (RA) can induce MDA-MB-468 apoptosis, also can act on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells to promote growth and metastasis. This suggests that RA can trigger pro-invasive actions in MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. In contrast, MDA-MB-468 cells will die under the action of AR. The pro-invasive effect of RA can be reversed by the statin cerivastatin [13]. Therefore, the effect of the medical drug on different types of breast cancer study can be done on the series of MDA-MB cells.

Figure3. Treatment with RA markedly increased cell invasion in MDA-MB-231 cells and inhibits the proliferation of MDA-MB-468 cells [13].
Conclusion:
So far, breast cancer cell lines have been widely used in breast cancer research, so researchers need to understand the characteristics of breast cancer cell lines and apply appropriate ones to their research. MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line is often used to study the effects of different factors on the occurrence and development of breast cancer because of its simple metastatic characteristics. In the future, we hope that MDA-MB- series cell lines will play an increasingly significant role in the research, diagnosis, and treatment of breast cancer.
AcceGen Human Breast Cancer Cell Line
AcceGen cultures and provides the most complete Human Breast Carcinoma Cell Lines. Among the total 19 MDA-MB- series of cell lines, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, MDA-MB-134-VI, MDA-MB-157, MDA-MB-175-VII, MDA-MB-361, MDA-MB-415, MDA-MB-435S, MDA-MB-436, and MDA-MB-453 are in AcceGen database now, and we are still trying to expand our cell line repository to better support your research.
Besides the MDA-MB-series cell lines, ZR-75-1, ZR-75-30, MCF7, CAMA-1, SK-BR-3, MX-1, and other featured Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines are also popular for breast cancer research. For more detailed information, please visit our website or contact [email protected].
References
1. Martino E, Vuoso DC, D’Angelo S, Mele L, D’Onofrio N, Porcelli M, Cacciapuoti G: Annurca apple polyphenol extract selectively kills MDA-MB-231 cells through ROS generation, sustained JNK activation and cell growth and survival inhibition. Sci Rep 2019, 9(1):13045.
2. CDCOrganization: Breast Cancer in Young Women. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dcpc/resources/features/breastcanceryoungwomen/2020.
3. Wang B, Xing Z, Wang F, Yuan X, Zhang Y: Fangchinoline inhibits migration and causes apoptosis of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncol Lett 2017, 14(5):5307-5312.
4. R Cailleau MO, QVJ Cruciger: Long-term human breast carcinoma cell lines of metastatic origin: Preliminary characterization. In Vitro 1978, 14:911-915.
5. Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T, Clark L, Bayani N, Coppe JP, Tong F et al: A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10(6):515-527.
6. Chen K, Satlof L, Stoffels G, Kothapalli U, Ziluck N, Lema M, Poretsky L, Avtanski D: Cytokine secretion in breast cancer cells – MILLIPLEX assay data. Data Brief 2020, 28:104798.
7. Li P, Butcher NJ, Minchin RF: Effect arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 on morphology, adhesion, migration, and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells: role of matrix metalloproteinases and integrin alphaV. Cell Adh Migr 2020, 14(1):1-11.
8. Tsai HY, Fu SL, Tseng LM, Chiu JH, Lin CH: hnRNPK S379 phosphorylation participates in migration regulation of triple negative MDA-MB-231 cells. Sci Rep 2019, 9(1):7611.
9. Ocana MC, Martinez-Poveda B, Quesada AR, Medina MA: Glucose Favors Lipid Anabolic Metabolism in the Invasive Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231. Biology (Basel) 2020, 9(1).
10. Gaglio D, Metallo CM, Gameiro PA, Hiller K, Danna LS, Balestrieri C, Alberghina L, Stephanopoulos G, Chiaradonna F: Oncogenic K-Ras decouples glucose and glutamine metabolism to support cancer cell growth. Mol Syst Biol 2011, 7:523.
11. Djeungoue-Petga MA, Lurette O, Jean S, Hamel-Cote G, Martin-Jimenez R, Bou M, Cannich A, Roy P, Hebert-Chatelain E: Intramitochondrial Src kinase links mitochondrial dysfunctions and aggressiveness of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10(12):940.
12. Lobos-Gonzalez L, Bustos R, Campos A, Silva V, Silva V, Jeldes E, Salomon C, Varas-Godoy M, Caceres-Verschae A, Duran E et al: Exosomes released upon mitochondrial ASncmtRNA knockdown reduce tumorigenic properties of malignant breast cancer cells. Sci Rep 2020, 10(1):343.
13. Mezquita B, Mezquita P, Pau M, Gasa L, Navarro L, Samitier M, Pons M, Mezquita C: All-trans-retinoic acid activates the pro-invasive Src-YAP-Interleukin 6 axis in triple-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells while cerivastatin reverses this action. Sci Rep 2018, 8(1):7047.

Copyright - Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are AcceGen™ All Rights Reserved – Full details of the use of materials on this site please refer to AcceGen Editorial Policy – Guest Posts are welcome, by submitting a guest post to AcceGen you are agree to the AcceGen Guest Post Agreement – Any concerns please contact [email protected]